Prokaryotic Gene Structure Chloe's Science
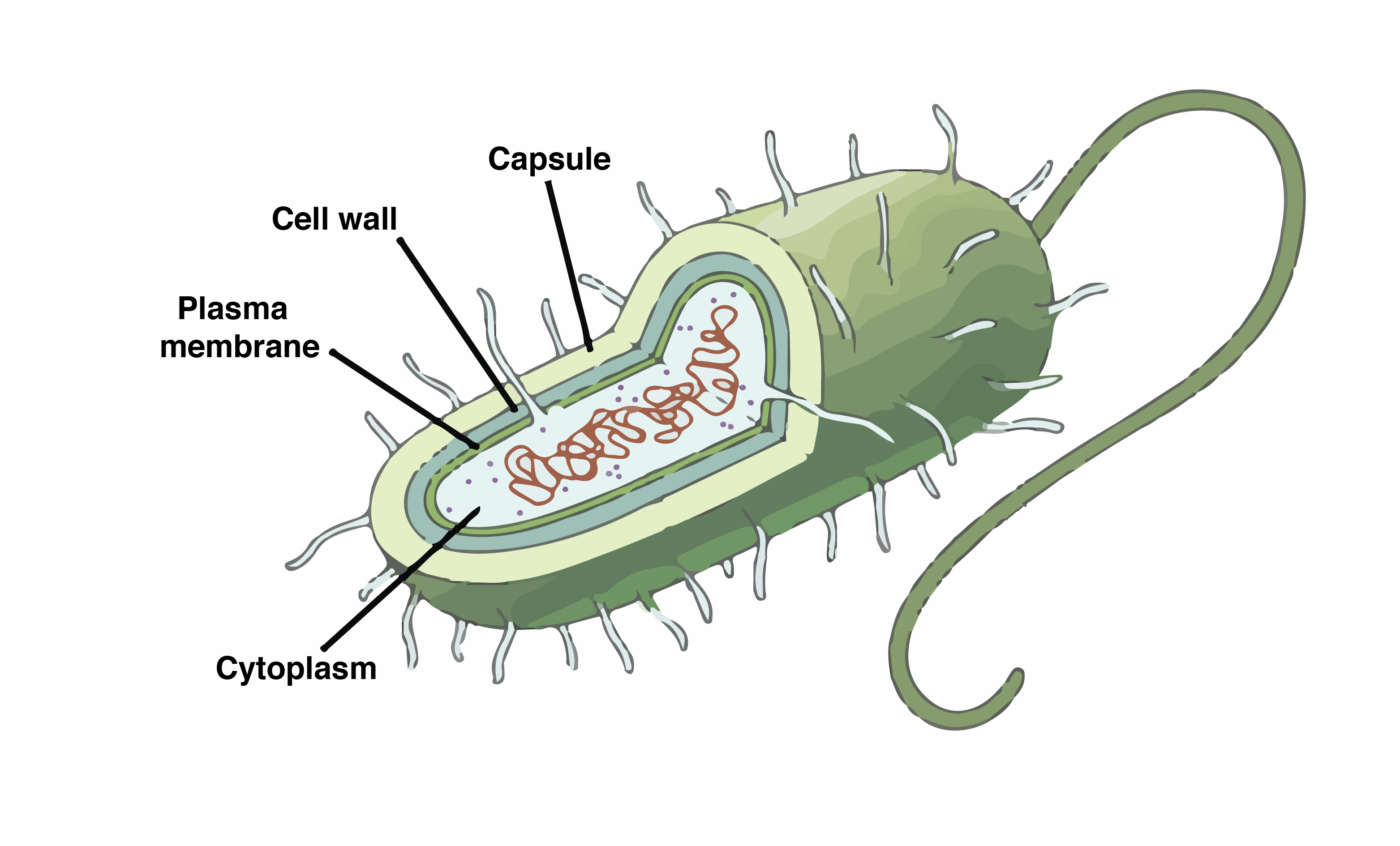
Summary. Prokaryotes are predominantly single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea. All prokaryotes have plasma membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA that is not membrane-bound. Most have peptidoglycan cell walls and many have polysaccharide capsules. Prokaryotic cells range in diameter from 0.1 to 5.0 μm.
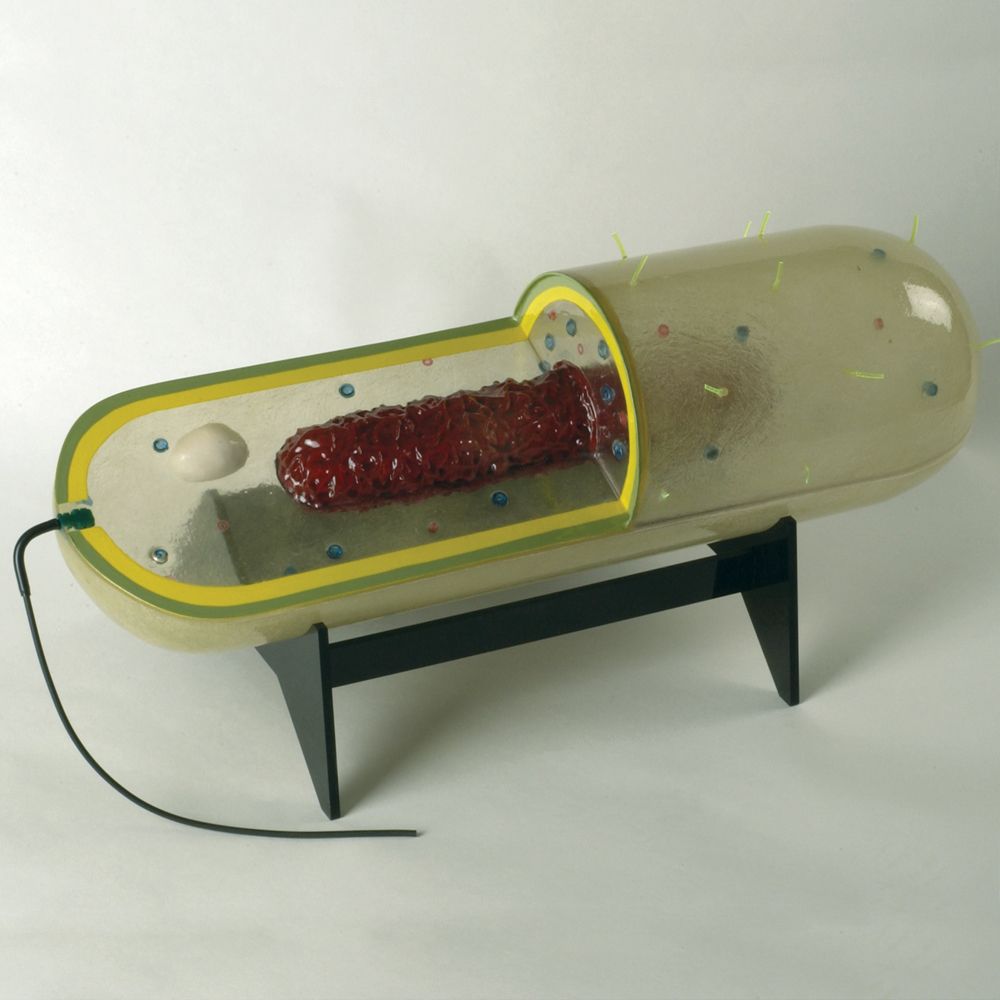

Staco Prokaryotic Cell Model
A prokaryotic cell is a type of cell that does not have a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Organisms within the domains Bacteria and Archaea are based on the prokaryotic cell, while all other forms of life are eukaryotic. However, organisms with prokaryotic cells are very abundant and make up much of Earth's biomass. Overview

Prokaryotic Cell Model YouTube
E. coli. Because of their comparative simplicity, prokaryotic cells (bacteria) are ideal models for studying many fundamental aspects of biochemistry and molecular biology. The most thoroughly studied species of bacteria is E.coli, which has long been the favored organism for investigation of the basic mechanisms of molecular genetics.Most of our present concepts of molecular biology.
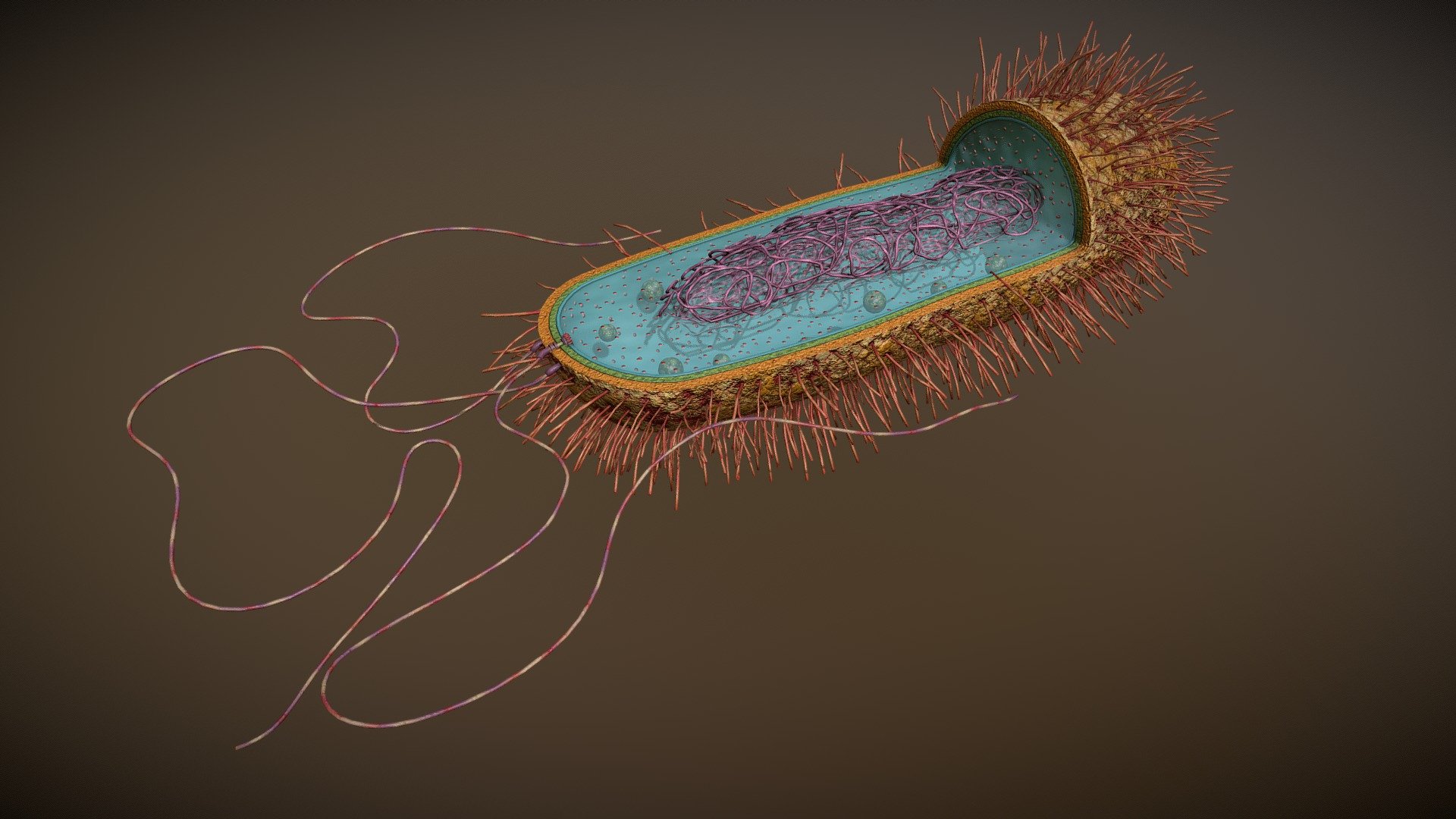
Prokaryotic Cell Structure 3D model by Vida Systems (objects1) [82bc108] Sketchfab
Most prokaryotes have a cell wall outside the plasma membrane. Figure 27.2.2 27.2. 2: The features of a typical prokaryotic cell are shown. Recall that prokaryotes are divided into two different domains, Bacteria and Archaea, which together with Eukarya, comprise the three domains of life (Figure 27.2.3 27.2. 3 ).
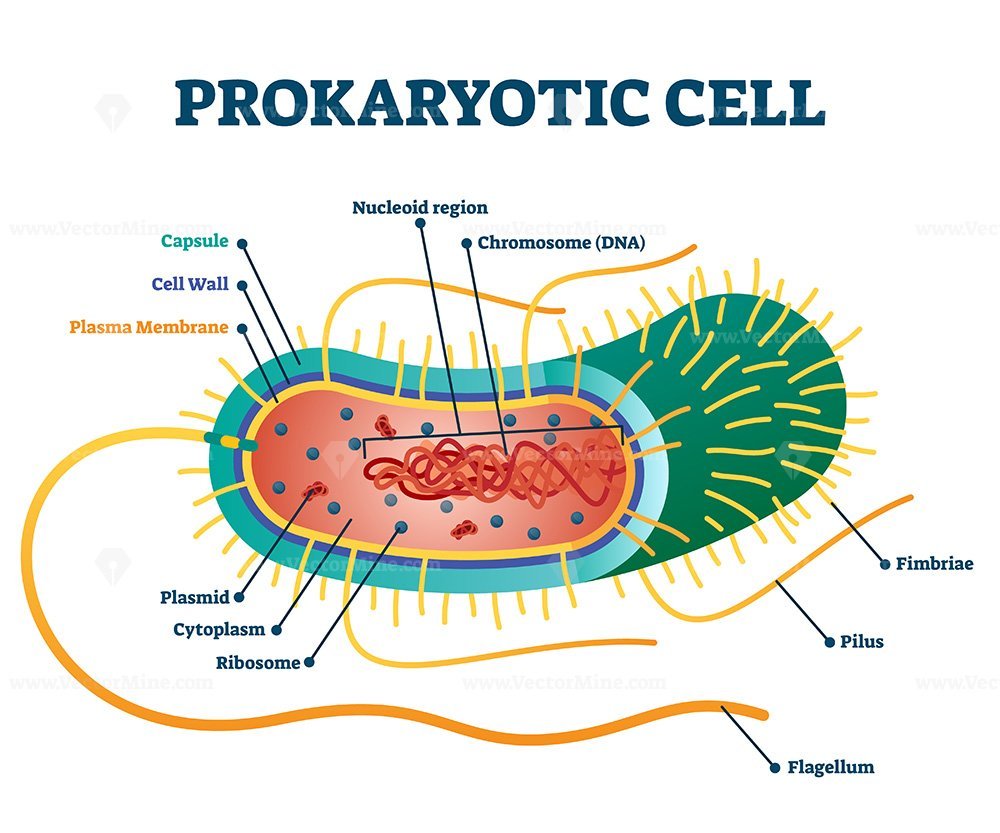
Prokaryotic cell structure diagram, vector illustration cross section labeled scheme VectorMine
The gap between the two DNA fragments is sealed by DNA ligase, which helps in the formation of phosphodiester bonds. Table 14.4.1 14.4. 1 summarizes the enzymes involved in prokaryotic DNA replication and the functions of each. Table 14.4.1 14.4. 1: Prokaryotic DNA Replication: Enzymes and Their Function. Enzyme/protein.
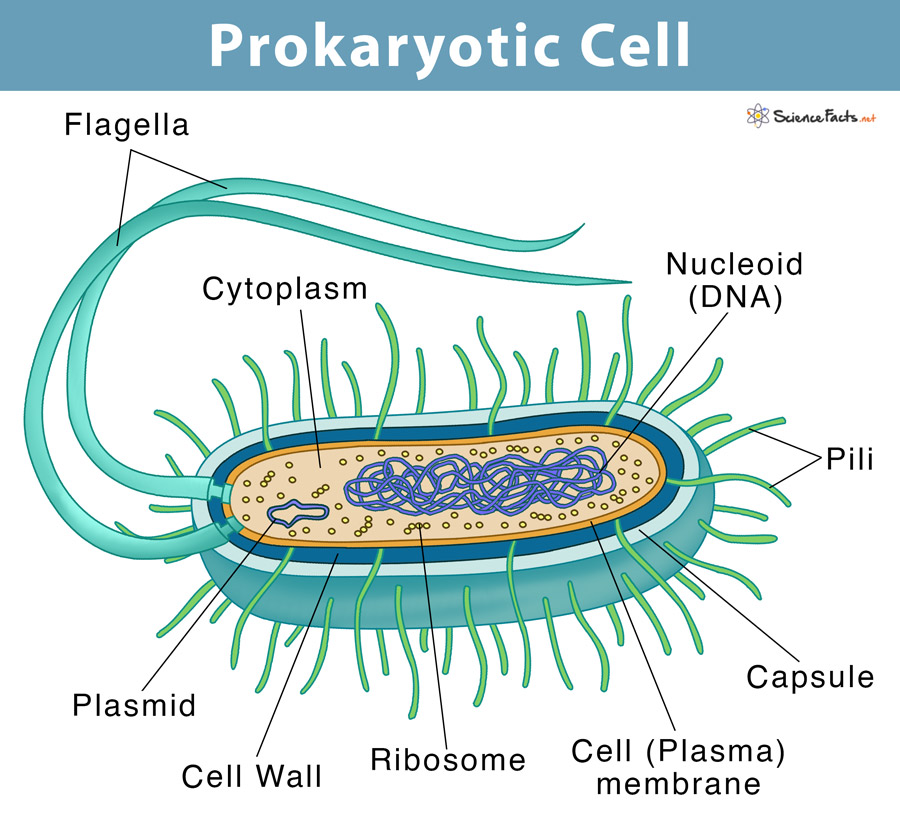
Prokaryotic Cell Definition, Examples, & Structure
A prokaryote is a simple, single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.

Prokaryotic Cell by zirzow Thingiverse Prokaryotic cell, Biology projects, Cell model project
A typical prokaryotic cell contains a cell membrane, chromosomal DNA that is concentrated in a nucleoid, ribosomes, and a cell wall. Some prokaryotic cells may also possess flagella, pili, fimbriae, and capsules. Common Cell Morphologies and Arrangements. Individual cells of a particular prokaryotic organism are typically similar in shape, or .
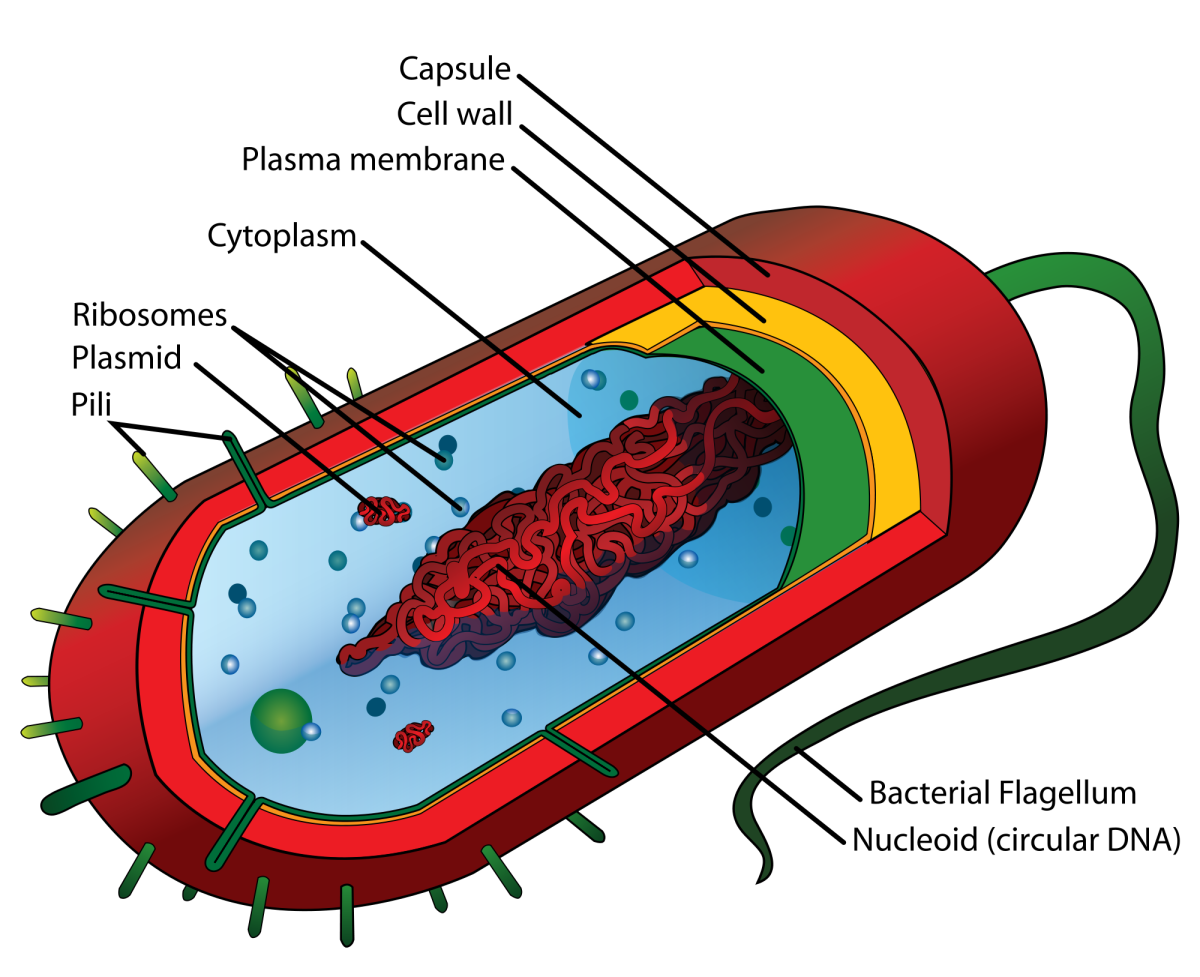
Prokaryotic Cell Structure A Visual Guide Owlcation
Diagram Components Reproduction Examples What is a Prokaryotic Cell? Prokaryotic cells are single-celled microorganisms known to be the earliest on earth. Prokaryotes include Bacteria and Archaea. The photosynthetic prokaryotes include cyanobacteria that perform photosynthesis.
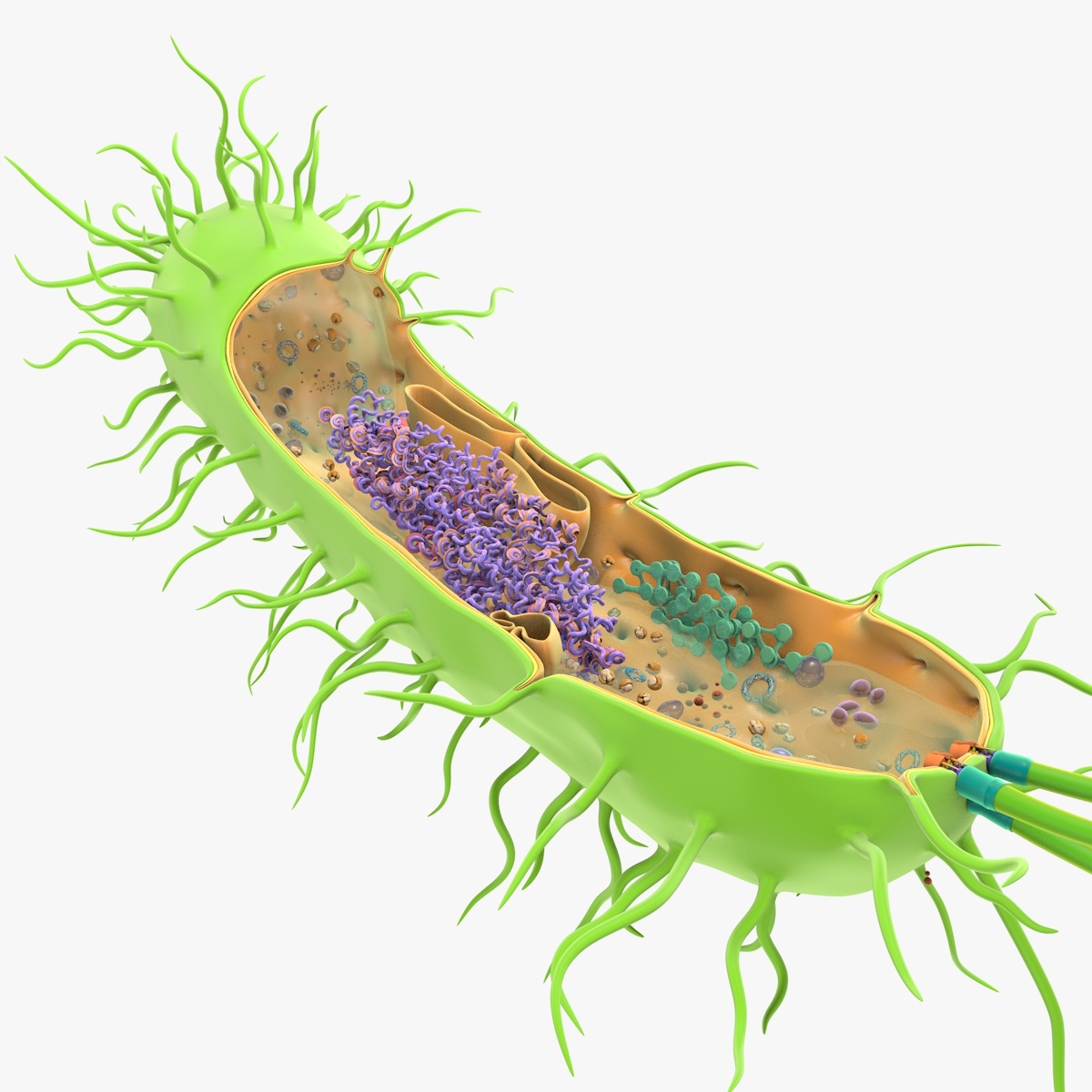
Prokaryotic cell ribosomes model 1149003 TurboSquid
A prokaryote ( / proʊˈkærioʊt, - ət /, also spelled procaryote) [1] is a single-cell organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membrane -bound organelles. [2] The word prokaryote comes from the Ancient Greek πρό ( pró) 'before' and κάρυον ( káruon) 'nut, kernel'.
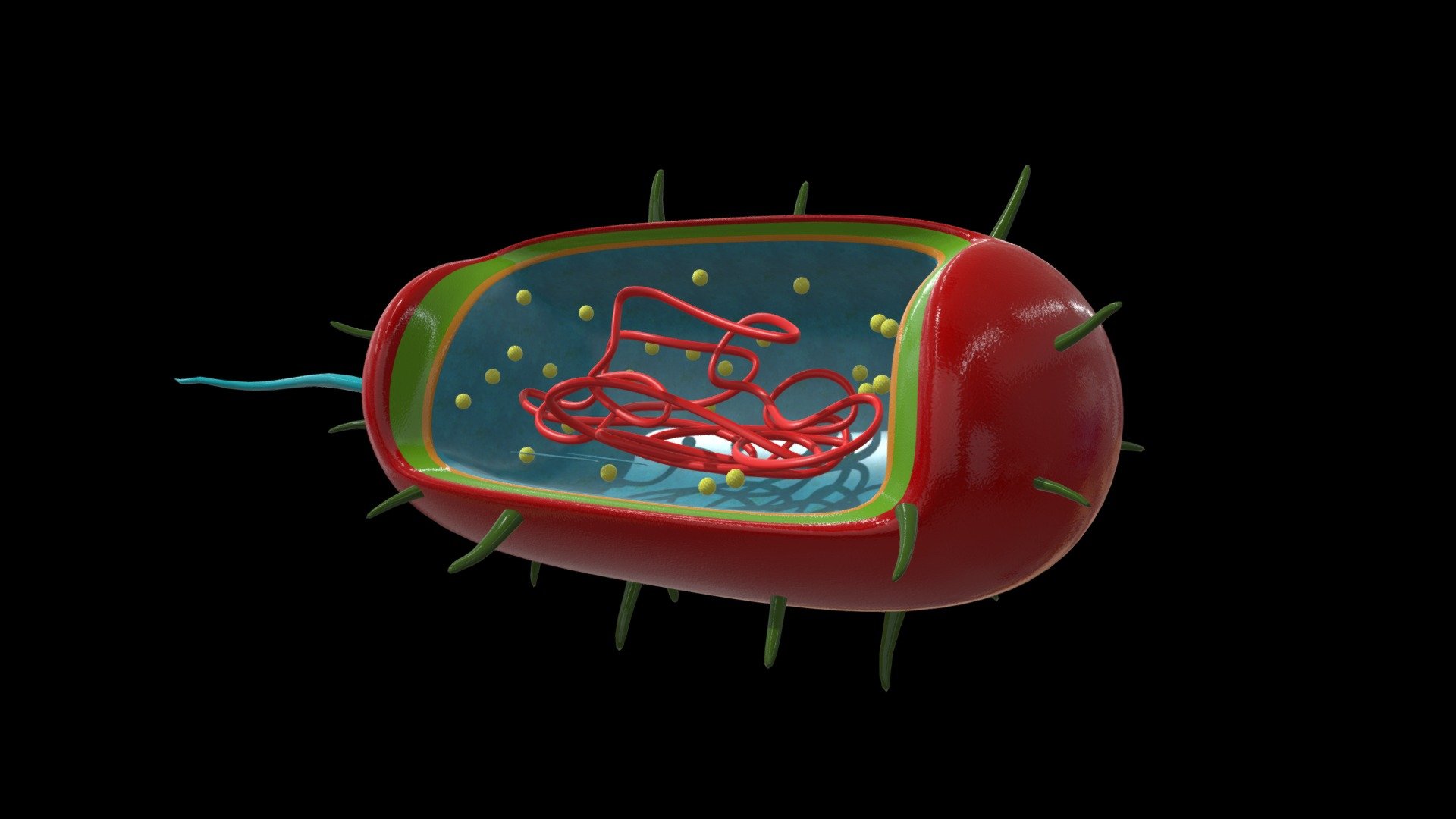
Prokaryote Cell 3D model by University of New England Archaeology (Melanie_FilliosUNE
5 Prokaryotic Cell 9.9k 2 8 View all Buy Prokaryotic-cell 3D models Prokaryotic-cell 3D models ready to view, buy, and download for free.

STL file Prokaryotic Cell・3D printer model to download・Cults
A. The prokaryotic cells have a nucleus, while the eukaryotic cells do not. The prokaryotic cells have cytoplasm, and eukaryotic cells do not. B. The prokaryotic cells have cytoplasm, and eukaryotic cells do not. The prokaryotic cells are much smaller than the eukaryotic cells. C. The prokaryotic cells are much smaller than the eukaryotic cells.
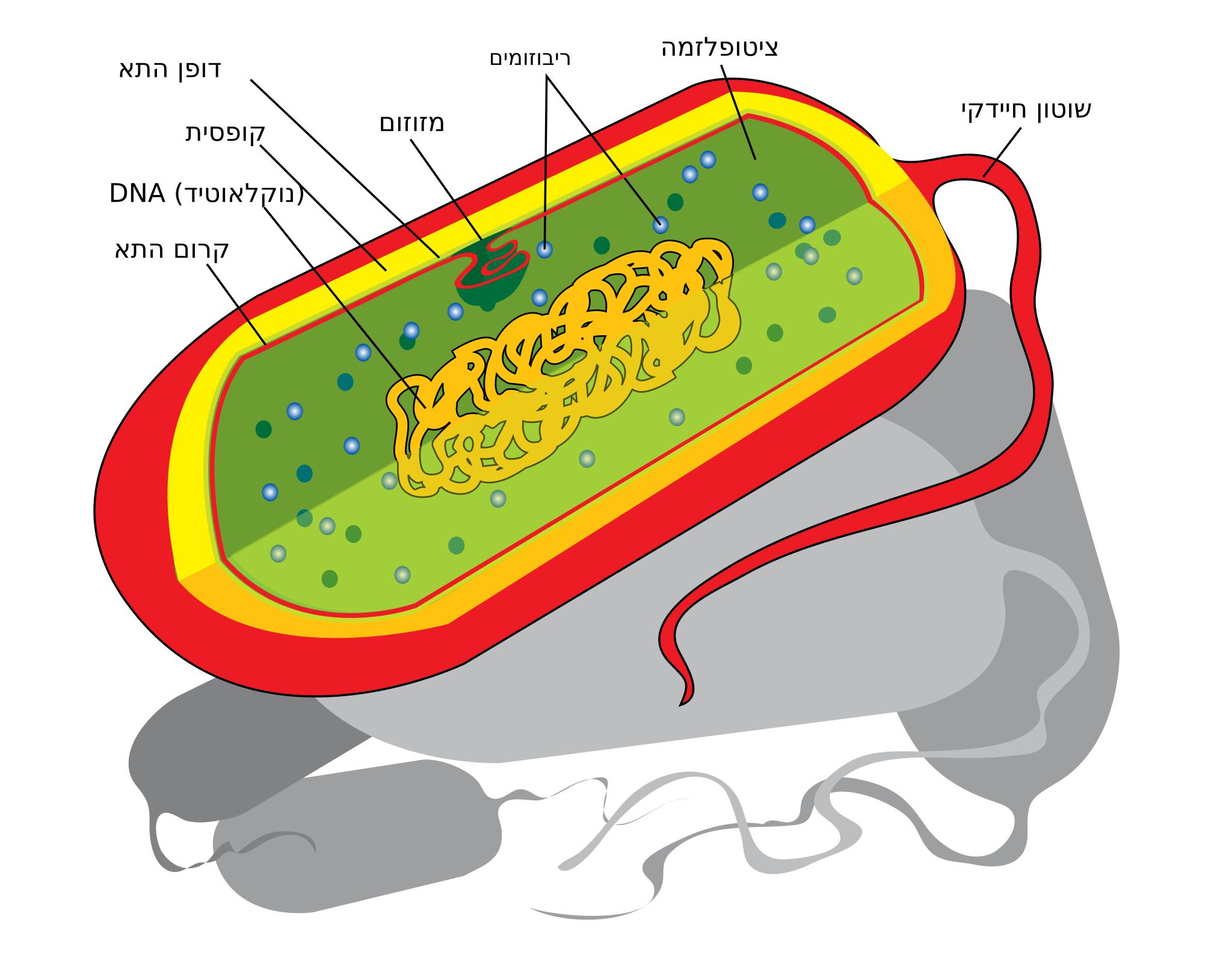
Free Images prokaryote cell diagram he
Prokaryotic cell transcriptomics has been limited to mixed or sub-population dynamics and individual cells within heterogeneous populations. Here the authors develop a 'TRANSITomic' approach.

Endosymbiotic Theory Ask A Biologist
Prokaryotic Cell Model Construct a three-dimensional model of a prokaryotic cell (bacteria). Your cell must include the following structures — cell wall, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, chromosome, ribosomes, pili, and capsule. DO NOT USE ANY FOOD OR PLAY DOUGH FOR YOUR MODEL! Be sure to: Label the parts of the cell with straight pin "flags"

FileProkaryote cellro.svg Wikipedia
Bacteria Bacteria are microorganisms made up of a single prokaryotic cell. There are two general categories of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Sometimes, organisms are referred to as prokaryotes or eukaryotes, based on the type of cell (s) that compose them. 1. Prokaryotes are small and lack membrane-bound nuclei

Prokaryote Detailed Pedia
Prokaryotic cells are not as simple as once thought. They have diverse and dynamic organelles that perform various functions and shape the cell. This article reviews the recent advances in the cell biology of prokaryotic organelles, such as membrane-bound compartments, protein-based structures and DNA segregation systems.

Prokaryotic Cell 3D Model Zirzow Gallery Art by Amanda Zirzow
1.11: Prokaryotic Cells. Distinguish between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells in terms of structure, size, and the types of organisms that have these cell types. Identify structures of bacterial cells in models and diagrams, including details of Gram-positive and Gram-negative cell walls and flagella.